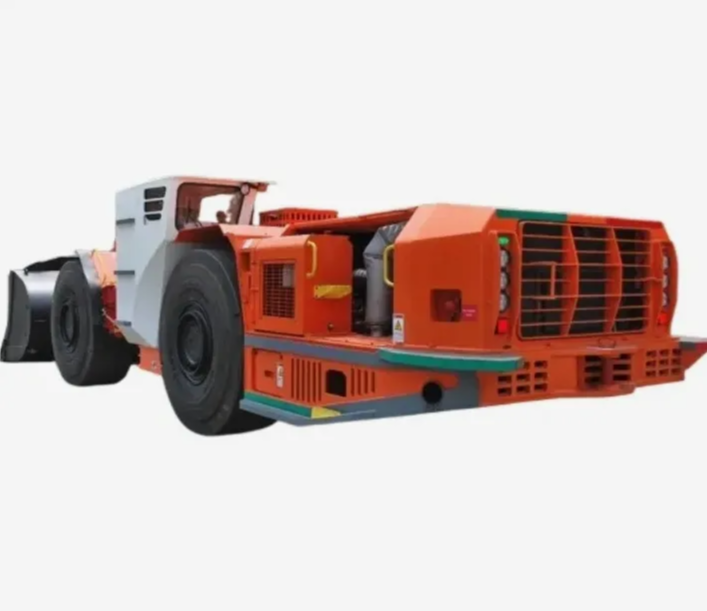
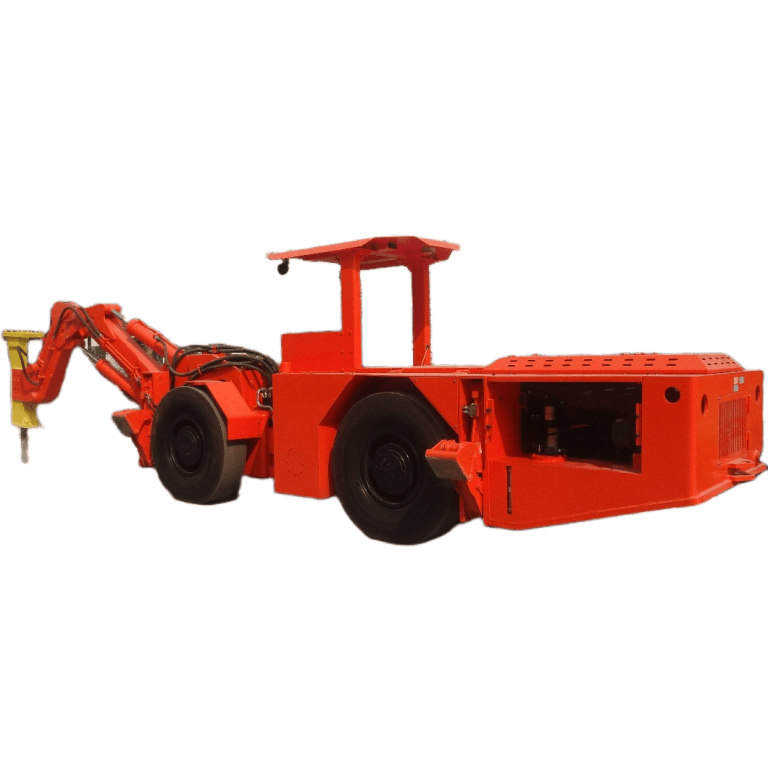
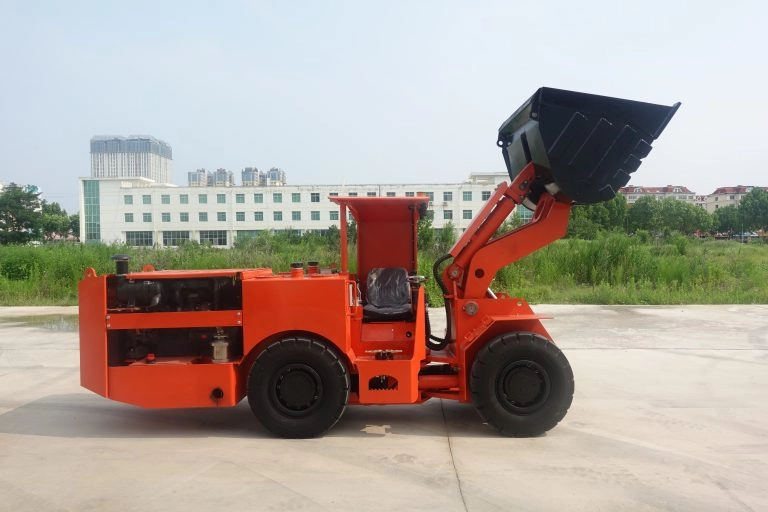
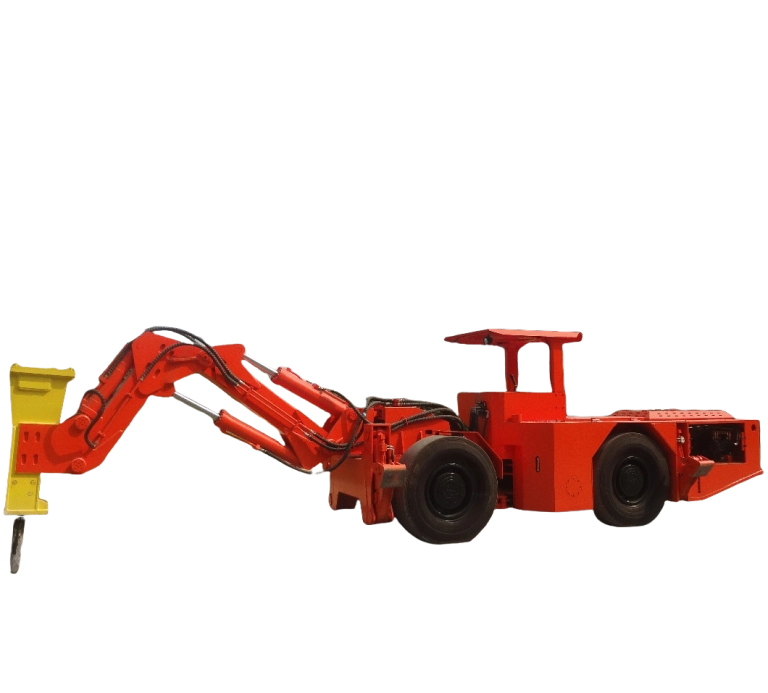
In underground mining, scooptrams handle tough jobs like loading and hauling ore through tight tunnels. Their performance directly impacts how much material moves each shift and keeps operations running smooth. Understanding the factors affecting scooptram performance helps mining teams spot issues early and keep equipment reliable. For a closer look at options built for these demands, check out our underground scooptram selections.
Many elements come into play, from the machine’s build to daily use in harsh settings. This guide breaks down the main ones, drawing from real-world mining scenarios where small changes lead to big gains in output.
Machine Design and Build Quality
The way a scooptram is put together sets the foundation for how it runs day in and day out. Strong designs handle rough ground better, cutting down on breakdowns.
Design choices affect everything from speed to load handling. For instance, compact sizes with tight turning radii let machines twist through narrow veins without getting stuck, which is common in older mines.
Bucket Size and Capacity
Bucket design stands out as a big player in underground loader performance. A bucket that’s too small means more trips to fill a truck, slowing the whole process. In one metal mine case, switching to a 2 cubic meter bucket cut cycle times by 15%, boosting daily tonnage.
But capacity isn’t just about volume. Shape matters too. Buckets with smooth curves dump faster, reducing spill and wear on hydraulics. Here’s a quick comparison of how bucket specs influence output:
| Bucket Capacity (m³) | Typical Load (metric tons) | Cycle Time Impact |
|---|---|---|
| 0.6 | 1.2 | Higher trips needed in large operations |
| 1.5 | 3.0 | Balanced for medium veins, fewer cycles |
| 3.0 | 6.0 | Faster in open areas, but needs wider tunnels |
Matching bucket to tunnel size prevents jams and keeps flow steady.
Designs with low weight-to-payload ratios also help. Lighter machines use less fuel and put less strain on tires, extending their life in wet, abrasive conditions.
Engine Power and Traction Forces
Power delivery keeps a scooptram moving under load. Engines around 120 kW push through muck piles without bogging down. Weak power shows up fast in steep inclines, where traction drops and wheels spin.
Traction force, often over 100 kN in solid units, grips slippery floors. Limited-slip differentials maintain hold on uneven rock, avoiding slips that waste time. In a hydropower tunnel project, machines with 155 kN traction cleared headings 20% quicker than lower-spec models.
Low-emission engines add another layer. They run cleaner, meeting regs while holding steady power in low-oxygen spots deep underground.
These specs tie into overall build. Rigid frames resist twisting, keeping alignment true over thousands of hours.
Operating Environment in Mines

No scooptram runs in a vacuum. Tunnel conditions test every part, from tires to hydraulics. Wet floors or dust change how máquinas handle loads.
Harsh settings demand adaptations. For example, in narrow veins, small turning radii—inner around 2800 mm—let operators navigate without constant reversing, which eats into shift time.
Ground Conditions and Tunnel Layout
Floor quality hits scooptram efficiency factors hard. Muddy or rocky ground increases resistance, forcing higher revs and burning more fuel. Smooth, graded paths let machines hit top speeds, up to 23 km/h in flat sections.
Tunnel width and height limit movement. Machines over 2 meters wide struggle in 1.8-meter drifts, leading to scrapes and downtime. Sharp turns amplify this; outer radii over 5000 mm work in open areas but fail in tight spots.
Dust and water add risks. Ventilation keeps air clear, but poor flow clogs filters, dropping power by 10-15%. Sealed cabs protect operators, letting them focus without health worries.
Material Type and Density
Ore density varies. Dense rock needs more shovel force—say 81 kN—to break free, while loose muck loads easy but can overflow buckets.
In gold mines with sticky clay, buckets fill slow, raising cycle times. Dry, fragmented material dumps quick but creates dust clouds that blind sensors.
Adapting to material keeps performance high. Buckets with teeth penetrate better in hard piles, cutting load time by seconds per scoop—adding up over a shift.
Environment shapes wear too. Abrasive quartz grinds tires fast, while soft coal eases strain. Teams track this to plan replacements.
Maintenance Routines and Parts Availability
Regular checks keep scooptrams at peak. Skipping them leads to failures that halt production for days.
Ground-level access simplifies tasks. Operators check fluids without climbing, reducing injury risks and speeding daily routines.
Scheduled Checks and Repairs
Daily maintenance catches small issues. Oil levels, tire pressure, and hydraulic lines—if off—cut factors influencing LHD performance like speed and lift.
In a 12-year mine study, fleets with weekly inspections saw 25% fewer breakdowns. Filters changed every 500 hours prevent clogs that sap power.
Parts quality counts. Durable axles with spring-applied brakes hold up in wet conditions, avoiding slips.
Impact of Downtime on Operations
Unplanned stops hurt. A broken torque converter idles the machine for hours, backing up hauls.
Quick diagnostics from control systems pinpoint faults fast. In one case, a monitoring setup cut troubleshooting from 4 hours to 30 minutes.
Spare parts on hand slash wait times. Mines stocking common items like seals resume faster, keeping tonnage steady.
Strong routines build reliability. They extend machine life, lowering costs per ton moved.
Operator Training and Handling Techniques
Even top machines falter with poor handling. Skilled operators squeeze more from equipment.
Training covers basics like smooth acceleration to avoid wheel spin. In tight tunnels, precise steering prevents wall hits.
Skills for Efficient Loading
Loading technique affects fill rates. Approaching piles at right angles maximizes shovel force, filling buckets full without overflow.
Operators who monitor gauges spot drops in pressure early, avoiding overloads that strain engines.
In training programs, new drivers learn to dump clean, reducing spill that requires extra cleanup passes.
Características de seguridad y ergonomía
Cab designs with good visibility cut errors. ROPS/FOPS protection keeps focus on tasks, not risks.
Controls that fit natural movements speed cycles. In long shifts, comfy seats reduce fatigue, maintaining sharp decisions.
Trained teams hit higher outputs—up to 20% more tons per hour in studies.
Technological Add-ons and Upgrades
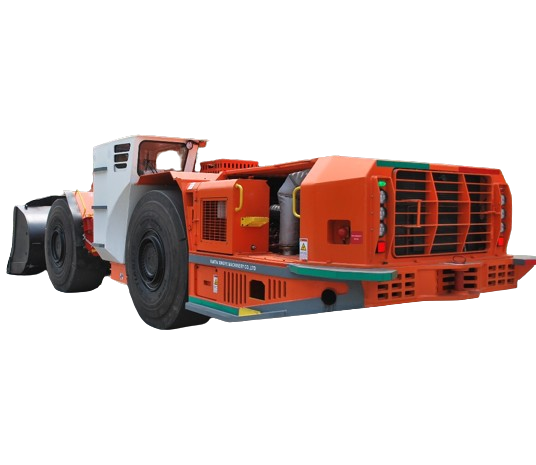

Modern features lift baseline performance. Automation-ready setups allow remote control in risky zones.
Intelligent controls track parameters, alerting to issues before they grow. This minimizes stops in high-production mines.
Boom geometry with high lift shortens cycles. Automatic gear shifting keeps momentum on ramps.
Upgrades like low-emission tech sustain power while cutting fumes, aiding ventilation-limited sites.
These additions make machines adaptable, handling varied jobs without major overhauls.
Acerca de Yantai Chi Hong Machinery Co., Ltd.
Yantai Chi Hong Machinery Co., Ltd. stands as a key supplier of underground scooptrams and related mining gear. Based in Yantai City, China—a hub for trackless equipment—they focus on building machines that emphasize safety, efficiency, and low costs. With certifications like ISO 9001:2015 and EU CE, their products meet global standards. They offer a range from compact loaders for narrow veins to larger units for tough applications, all backed by a team dedicated to innovation and customer support. For more on their lineup, visit their products page.
Conclusión
Grasping these factors affecting scooptram performance equips mining operations to run smoother and safer. From solid design to smart maintenance, each piece contributes to higher output and fewer headaches. By addressing them head-on, teams can push equipment harder while extending its life, ultimately driving better results underground.
Preguntas frecuentes
What are the main factors affecting scooptram performance in narrow tunnels?
Tight spaces highlight design elements like small turning radii and compact dimensions. Ground conditions also play a role—muddy floors reduce traction, so regular grading helps maintain speed and load efficiency.
Cómo does maintenance influence underground loader performance?
Routine checks prevent small problems from becoming big ones. For example, changing filters on schedule avoids power loss, and ground-level access makes daily tasks quicker, keeping machines ready for full shifts.
Puede operator skills really impact factors influencing LHD performance?
Yes, trained operators load faster and avoid damage. Smooth handling in rough spots cuts wear, and using safety features like enclosed cabs keeps focus sharp, often boosting daily tonnage by double digits.
What environmental factors affect the performance of an underground chaqueta?
Dust, water, and ore type all matter. High dust clogs systems, while dense materials demand more force. Good ventilation and matched buckets help counter these, ensuring steady runs.